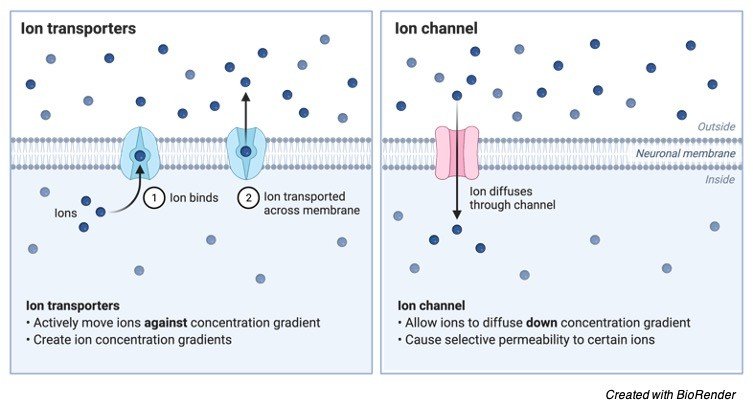
Their efficiency is less than that of channel proteins as during transportation there is a conformational change in these proteins. A model of a channel protein and carrier proteins is shown in Figure below.
Carrier Proteins Definition Function And Examples
Temperature and saturation affect the carrier proteins.

. A number of inherited diseases involve defects in carrier proteins in a. Structural proteins are especially important in larger cells. C After a carrier has transported a molecule it is unable to transport any more.
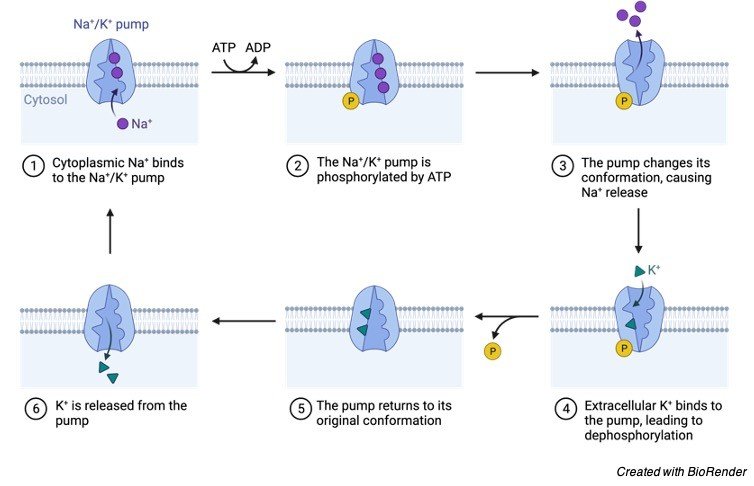
It moves three Na ions into the cell while moving two K ions out of the cell. The sodium-potassium pump begins with its sodium binding sites facing the inside of the cell. B It is represented by the glucose carrier that can transport hundreds of molecules a second.
For example GLUT1 is a named carrier protein found in almost all animal cell membranes that transports glucose across the bilayer. The most famous example of a primary active transport protein is the sodium-potassium pump. This takes place against the concentration gradient and 1 ATP is consumed for this process.
Is One type of transporter is a channelcarrier enzymatic protein these allow only certain specific molecules to pass through them and the work using simple diffusion. It is this pump that creates the ion gradient that allows neurons to fire. Active transport uses proteins from the carrier.
Carrier proteins carry the ion or molecule across the membrane by changing shape after the binding of the ion or molecule. What are some examples of carrier proteins used in passive transport. Carrier proteins are a type of membrane proteins which helps in transporting molecules from outside to inside or vice-a-versa.
Biology Molecular Biology Basics Proteins. Collagen is the most abundant example of a structural protein and accounts for around a quarter of all proteins in the body. Serum albumin carries fats in your bloodstream while myoglobin absorbs oxygen from hemoglobin and then releases it to the muscles.
The action occurs on the side of the membrane facing the higher concentration of the passenger molecule. Facilitated diffusion through the cell membrane. Once the protein captures its passenger it shapeshifts to funnel the molecule to the proteins other end.
Others may add up. Carrier protein because it have active transport and bimds specific protein while channel protein have passive and transport not View the full answer Transcribed image text. I only know these two.
They are used to provide an internal structure to the cell and are sometimes involved in cell movement. The main difference between channel and carrier proteins is that channel proteins have a fixed conformation in the cell membrane whereas carrier proteins flip between two conformations while transporting molecules. They carry the molecules change the confirmation of the molecules and release the molecules to the other side.
- Vesicle is a circled shaped membrane bound used to transport substances within a cell it carriers a certain fluid of substance and is involved in Exocytosis and Endocytosis. The glucose transporter was initially identified as a 55-kd protein in human red blood cells in which it. Examples of Facilitated Diffusion.
Carrier proteins are involved in passive and active transport. It plays an important role in the uptake of glucose by the cell. Another notable example is the Na -dependent glucose transporter which is active in the gastric mucosa and in the renal tubules.
Under the proper conditions a passive carrier protein will widen at one end to allow entry of a suitable molecule. These are present on the cell membrane. Structural proteins are also found in cells.
For mainly big polar molecules facilitated diffusion is used which cannot cross the phospholipid bilayer as they are hydrophilic polar molecules. Hemoglobin for example carries oxygen to body tissues from the lungs. There are certain transmembrane proteins that help in the movement of solutes and ions.
Myoglobin seems to function to give extra storage space for oxygen in the muscles which is useful for organisms that need to hold their breath for a long time. For example whales and seals have muscles with very high levels of myoglobin which explains why they can stay underwater without breathing for so long. This article explains 1.
If all of the protein carriers are being used it may become saturated. See answer 1 Best Answer. D Facilitated transport requires expenditure of chemical energy and is therefore active transport.
- Transferrin Carbonic anhydrase serum albumincytochromes. In biology some substances are hydrophilic and proteins from membranes provide a way. Examples of carrier proteins.
The carrier proteins that transport molecules by primary active transport are always coupled with ATPase. Cytochromes operate in the electron transport chain as carrier proteins for electrons. These sites attract sodium ions and hold onto them.
The Plasma Membrane Na -K Pump Is an ATPase. The most common example of primary active transport is the sodium-potassium pump. Protein is an example which is made out of amino acids lipids fatty acids and glycerol.
Some Ca 2 and H Pumps Are Also P-type Transport ATPases. Other specific carrier proteins also help the body function in important ways. E One carrier protein can carry a variety of different molecules.
Na -driven Carrier Proteins in the Plasma Membrane Regulate Cytosolic pH. An Asymmetric Distribution of Carrier Proteins in Epithelial Cells Underlies the Transcellular Transport of Solutes. 1 Answer Anuj Baskota Oct 20 2015 Some are Glut1 Sodium Potassium pump etc.
Three Na ions are pumped out of the cell and two K ions are pumped inside the cell. Characteristics Structure Role. Calbindin is another transport protein that facilitates the absorption of calcium from the intestinal walls.
What are Channel Proteins. The uptake of glucose which serves as a primary source of metabolic energy is one of the most important transport functions of the plasma membrane and the glucose transporter provides a well-studied example of a carrier protein. Example is GLUT protein which helps in transporting glucose to cell.
Sodium-potassium pump helps in maintaining the cell potential. The Na-K-2Cl carrier protein is a notable example of a symport cotransporter. What elements make up proteins.
It is very specific meaning only certain ions or molecules are transported by a given carrier. In order to adjust the shape of the carrier protein energy is used. It plays a vital role in salt secretion in the secretory epithelia cells along with renal salt reabsorption.

Learn About Carrier Proteins Chegg Com

Carrier Protein Definition Function And Examples Biology Dictionary

0 Comments